Agency SE-ERGO
📧 agencijaseergo@gmail.com
The study of schedule of a technological operation reveals the schedule that allows a shorter path of movement and optimal sequence of grips and movements in the operation. Better schedule and sequence lead to the increasing of labour productivity and better humanization in work, as well as better utilization of existing resources, shortening the total length of moving the objects of work, reducing the number of grips, shortening the duration of the operation.
Organizational
model is different from the production technology and it can be made in a
written form or acquired during a long series of repetitions, and it is caused
by:
•
workplace must have the optimal size,
•
working conditions should correspond to standards,
•
equipment should enable work in a standing or sitting position (employee
elects)
•
equipment should be located in the optimal zone is selected according to the
frequency of handling,
•
arrange the equipment to provide the optimal sequence of movements in the
operation and
•
arrange the equipment for supplying the workplace so that it should be optimal
in relation to employees and inter phase transport.
 |
| Workers position in workplace |
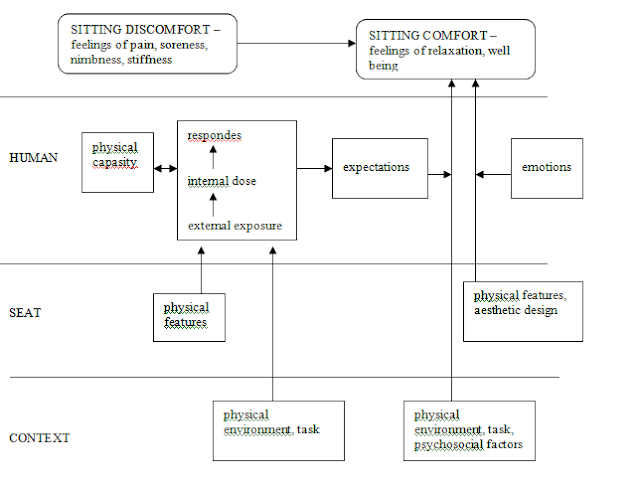 |
| Worker position diagram |

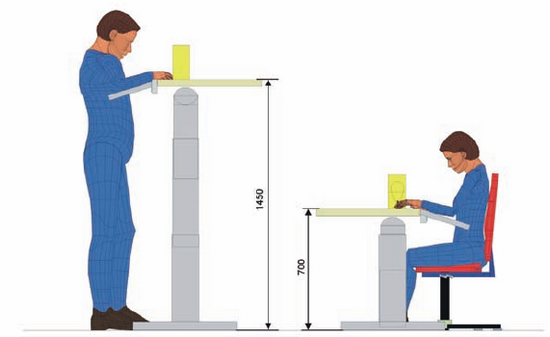 |
| Different body positions during working |
Read and download new article Ergonomics in Sewing Room in Journal of Textile Science & Engineering:
http://omicsgroup.org/journals/ergonomics-in-sewing-room-2165-8064.1000e123.php?aid=27966
 Ergonomics in the Garment Industry discusses the importance of
ergonomics in the garment industry, with a detailed scientific analysis and
examples from the garment industry. Application of ergonomics through the
standardization of micro and macro environment in the garment industry provides
an example of how to design the present and future processes; increases the
efficiency and productivity of production; improves health, safety and comfort
of people in the working environment.
Ergonomics in the Garment Industry discusses the importance of
ergonomics in the garment industry, with a detailed scientific analysis and
examples from the garment industry. Application of ergonomics through the
standardization of micro and macro environment in the garment industry provides
an example of how to design the present and future processes; increases the
efficiency and productivity of production; improves health, safety and comfort
of people in the working environment.